Global Methane Emission and Consumption
Methane (CH4), a colourless and odourless potent green house gas (GHG) contributing up to one third to the total global GHG emissions, has been considered as main culprit behind the global warming and consequently the climate change. As it absorbs infrared radiation so contributes about 15 to 20% in existing the earth temperature. The increasing concentration of CH4 in the environment is great cause for concerns because its global warming potential is up to 30 times greater than carbon dioxide (CO2).
It means increment of CH4 into the environment is about 30 times more effective in increasing global temperature than adding equal mass of CO2. In last couple of centuries, the CH4 atmospheric level has increased significantly because of an imbalance between global emission and consumption across different ecosystems.
The reports of Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) dictated that the atmospheric concentration of methane has been doubled during past 200 years and its concentration is rising by an average rate of 1% per year over the past few years. The atmospheric level of CH4 has been reached up to 1840 ppb from 700 ppb since 19th century i.e. the current atmospheric amount of CH4 are 2.5 times higher than pre-industrial concentrations. So, it is important to find out the various ways that may be beneficial in balancing the atmospheric methane level at global level.
CH4 emission at global level
CH4 is emitted from both the natural and anthropogenic sources around the globe. The anthropogenic activity is mostly responsible for the major part of global CH4 emissions, which my comprise up to the 63% (~566 Tg CH4/year). However the remaining emissions are carried out naturally (208 Tg CH4/year). Anthropogenic CH4 emissions are generated by the agricultural livestock, paddy cultivation, fossil fuels, waste practices, landfills, coal mining, natural gas distribution and biomass burning.
Whereas natural sources comprise wetlands, oceans, rivers, lakes, estuaries, gas hydrates geological sources, vegetation including terrestrial plants, wildfires, arthropods, wild animals and permafrost, etc (Figure 1). The anthropogenic CH4 production has increased steadily since the dawn of the industrial revolution.
Figure 1: Chief methane emitters at global scale (Mt/yr) (Source: IPCC)
Biological CH4 fermentation (MF)
Biologically CH4 is emitted by anaerobic bacteria called as methanogens and the process may be termed to as methanogenesis. In water logged and swampy places, CH4 is produced as the terminal step of the anoxic (absence of oxygen) decomposition of organic matter generating CH4 and CO2.
The anaerobic decomposition of organic matter and generation of methane in flooded places involves mainly through (a) polymers hydrolysis by hydrolytic organisms, (b) action of fermentative bacteria to form acid from simple organic compounds, (c) formation of acetate from metabolites of fermentations by homo-acetogenic or syntrophic bacteria, and (d) CH4 formation from H2/CO2, acetate, simple methylated compounds or alcohols and CO2.
MF is a versatile biotechnology able to convert polymeric materials to CH4 and CO2 anaerobically and achieved by the successive breakdown of polymers with a variety of unicellular organisms including acidogens (fermentative microbes), acetogens (acetate-forming microbes), methanogens and hydrogen-producing bacteria. Anaerobic bacteria play a very significant role in the formation of stable atmosphere at different stages of methane fermentation.
For the advantageous point of view, MF offers an efficient means of pollution abatement and provides superior way than the results achieved via traditional aerobic procedures. Although, the process is reported and used since 19th century, but the interest has only recently focused. It has been used for the treatment of excess sludge released from sewage-treatment plants. The MF technology has since been urbanized to treat waste waters, discharged from distilleries, tanneries, antibiotic and baker’s yeast manufacturing units.
Methanogens (methane generating bacteria)
Methanogens are spherical (coccoid) or rod shaped (bacilli) Archaebacteria. They are anaerobes and are very sensitive to the presence of very low level oxygen i.e. cannot survive under aerobic environment. There are over 50 species of methanogens have been isolated from waterlogged, sediments and many such places. Despite this methanogens also thrive in the stomach of ruminants and produce CH4 from CO2 and hydrogen released by other microbes residing.
Some examples of methanogens are: Methanococcus, Methanoculleus, Methanosarcina, Methanoplanu, Methanospirillum etc. However, Methanosarcina barkeri have been reported to contain superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme (which save organisms from the lethal effects of oxygen) and may survive longer than the others in the presence of O2. Moreover, some species use CO2 to sustain life called hydrogenotrophic.
CH4 consumption at global level
In global perspective, CH4 is oxidised by chemical and biological processes. The main sinks of CH4 are photochemical oxidation in atmosphere and microbial consumption at or near the sites of emission. Approximately 90% of the atmospheric CH4 is oxidized chemically within the tropospheric region with free hydroxyl radicals ‘the detergents of the atmosphere’.
Moreover, aerobic upland soils are the second major biological consumers for CH4 due to the presence of methanotrophic bacteria. Methanotrophs (CH4-oxidising bacteria, MOB) are the unique biological entity on earth scavenging CH4 biologically and play a very vital role to mitigate significant amount global CH4 load. It is reported that soil methanotrophic bacteria are associated with the removal of 10-40 Tg CH4/year, which comprises up to 6-10% of the global CH4 consumption.
The methanotrophs associated with the roots of rice paddies oxidise about 10-30% of the CH4 emitted by methanogens in rice field, which are one of the leading producer of potent GHG.
Figure 2: CH4 emission and consumption in environment
CH4 scavengers (CH4 eating bacteria)
Methanotrophs are diverse groups of gram-negative bacteria. They are sole biological sink of CH4 with proficiency of using CH4 for their carbon and energy needs. They are cosmopolitan and can be isolated from a wide variety of environments including extreme conditions. On the basis of CH4 oxidising pathways they have been divided on into type I (use RuMp patway, includes Methylomonas, Methylosphaera, Methylomicrobium, Methylosarcina, Methylobacter, Methylocaldum, Methylococcus, Methylohalobius, and Methylosom) and type II (use Serine pathway, includes Methylocystis, Methylocella, Methylocapsa and Methylosinus). Moreover, recently discovered Verrucomicrobia may be referred as type III.
Methanotrophs contain CH4 monooxygenase (MMO) enzyme to oxidise CH4 into CO2 through different steps (Figure 2). There are two distinct forms of this enzyme, the membrane-bound particulate CH4 monooxygenase (pMMO) and the cytoplasmic soluble methane monooxygenase (sMMO).
Figure 3: CH4 oxidation pathway (MMOs: CH4 monooxygenase; MDH: methanol dehydrogenase; MDH: formaldehyde dehydrogenase; FADH: formate dehydrogenase; FDH)
Reforestations of waste lands can contribute in CH4 mitigation
The world human population has been increased up to 250% in last six decades with a boom of 2.6 to 7.2 billion and is expected to cross 9.6 billion by the end of year 2050. In order to provide food for all, the production of cereals needs a leap of nearly 50% annually. This difficult goal puts heavy pressure on agriculture to gain food security. To attain large surface area for agriculture land expansion putting heavy load on the forests.
The conversion of natural subtropical forest to farmland lowers the CH4 sink capability of soil. However, the same may be recovered after afforestation. Addition of inorganic fertilizers into fields also disturbs the CH4 sink activity. In addition, the developmental activities are going throughout the world leading to cut down of trees as well as releasing large amount of GHGs into the atmosphere.
Since, we cannot stop the blind run of development immediately, therefore, should think positively regarding the safety measures and remedies. A 10% increase in CH4 consumption rate may stabilize the current concentration of this potent GHG in the environment.
Many scientific reports summarize that the forest soil is best suited for the growth and functioning of methanotrophs and consequently mitigating global CH4 budget (Figure 4). It has been discussed that afforestation, reforestation, improved forest management and reduced deforestation considerably contributes to reductions in excess atmospheric CH4 load.
Figure 4: CH4 sink activity across different land use types (Source: Singh and Gupta, 2016)
Applied facets of CH4 scavenging bacteria
CH4 scavenging bacteria (methanotrophs), an important group of microbes, are generally considered to consume the CH4 (a potent green house gas) in atmosphere. The CH4 consuming unique enzyme methane monooxygenase (MMOs) present in these bacteria not only destroy the CH4, but also have capability to degrade/metabolise several pollutants viz.
heavy metals (Cr, Cd), aliphatic hydrocarbons (dichloroethylene, trichloroethylene, vinyl chloride and chloroform), halogenated hydrocarbons, halogenated benzenes, toluene, styrene, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons and transition metals, phenanthrene, anthracene, and fluorine, neurotoxin methyl mercury, etc (Figure 5). So, these unique bacteria in nature with unique enzyme are contributing significantly at global level in the management ecosystems and environment.
Methanotrophic community structure associated with roots (rhizospheric region) also play beneficial role in the growth and development of plants. They can be used as single-cell protein, biopolymers, and nano-technological applications, soluble metabolites, lipids, growth media, and vitamin. Similar to other microorganism’s methanotrophs can also be genetically engineered to produce carotenoids, enzymes, etc. Methanotrophic bacterial cultures can be employed for wastewater denitrification, making of biosensors, and possibly electricity generation.
Figure 5: Versatility of methanotrophs in nature
According to food and agriculture organization (FAO) rice contributes over 43% to the country’s food grain production. India is second leading country in world with respect to production of paddy after China. China has more than 43 million ha of land area under paddy cultivation and produces approximately 125 million tonnes of rice. It is reported that flooded paddy fields are responsible for emission of CH4 to the environment.
So, other countries are blaming India regarding the contribution of significant increment of CH4 to the atmosphere because of the vast flooded paddy agriculture area. At the same it has been reported that dry land paddy agriculture showed CH4 consumption instead of CH4 emission. Therefore, Indian scientists are involved to develop new high yielding dry land rice varieties that may contribute significantly in CH4 reduction rates in future paddy agriculture.
In present scenario, we have been intensely involved in the blind run so called development, which is also adding different problems such as global warming, climate change, cancers, skin and lung problems, etc. Therefore, it is needed to adapt sustainable growth patterns for the safety and security of future generations. Application of biofertilizers, reforestation of disturbed land and afforestation, etc may be a good alternative to sustain the living beings and consequently reduction of CH4 emission in environment globally (Figure 6).
Figure 6: A hypothetical model demonstrating anthropogenic activities CH4 emission

















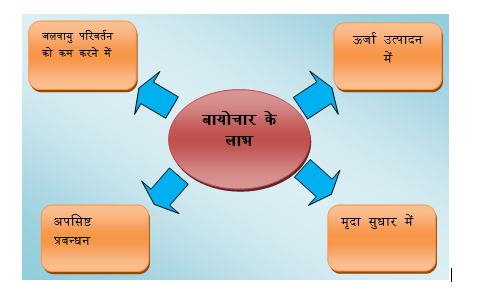 चित्र: पर्यावरण में बायोचार के लाभ
चित्र: पर्यावरण में बायोचार के लाभ